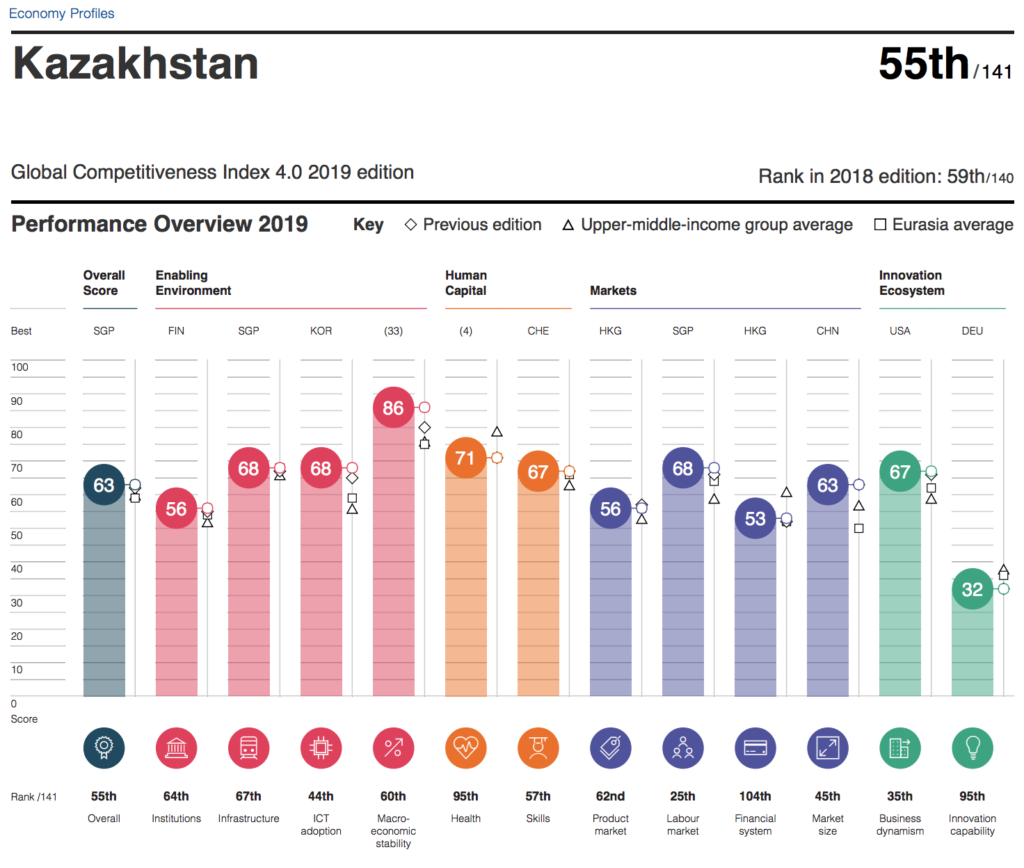
NUR-SULTAN – Kazakhstan moved up four spots to 55th out of 141 countries in the Global Competitiveness Index published Oct. 9 by the World Economic Forum. The report assesses drivers of productivity and long-term economic growth.
Kazakhstan, with a score of 63 points, is positioned between Uruguay and Brunei Darussalam.
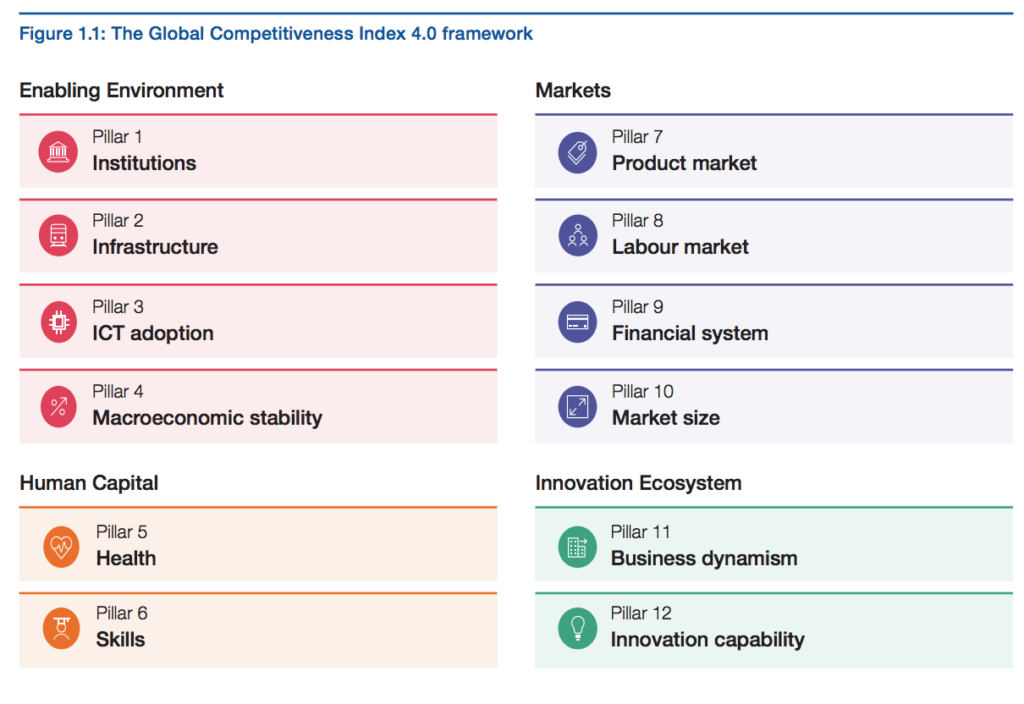
The report, in its 40th year, organises 103 indicators, such as digital skills, inflation and social capital, into 12 pillars – institutions, infrastructure, information and communication technology (ICT) adoption, macroeconomic stability, health, skills, product market, labour market, financial system, market size, business dynamism and innovation capability.
Singapore, named the world’s most competitive economy, scored 84.8 points to overtake last year’s leader, the United States, which moved to second place. Hong Kong, the Netherlands and Switzerland round out the top five.
Singapore ranks first in terms of infrastructure, health, labour market functioning and financial system development. With the city-state leading the ranking, the East Asia and Pacific regions have become the most competitive in the world, followed by Europe and North America.
Kazakhstan’s highest score was in the shareholder governance indicator in the institutions pillar. The country’s institutions, which were assessed across security, social capital, checks and balances, public sector performance, transparency, property rights, corporate governance and future government orientation, ranked 64th.
The nation ranks 67th in terms of infrastructure and 44th in ICT adoption, performing relatively better than the upper-middle-income group average.
Kazakhstan received its highest assessment in macroeconomic stability ranking 60th with 86 points. The country, which was second after Russia in most competitive economy in Eurasia, placed 95th in health, 57th in skills, 62nd in product market, 25th in labour market, 104th in financial system strength, 45th in market size and 35th in business dynamism.
Kazakhstan fell short in the innovation capability pillar, where it received its lowest score of 31 and ranked 95th.
“Focusing on financial development and innovation capability would help the region (Eurasia) to achieve a higher competitiveness performance and advance the process towards structural change,” said the report.
It noted the countries that invest heavily in research and development, enhance the skills base of their workforce, develop new infrastructure and introduce new technologies, are more likely to advance in the competitiveness frontier.
“The report shows that those countries which integrate into their economic policies an emphasis on infrastructure, skills, research and development and support those left behind are more successful compared to those which focus only on traditional factors of growth,” said World Economic Forum Chair and founder Klaus Schwab in the report.
The gap between countries remains significant and the uncertainty is fuelled by the changing geopolitical context and escalating trade tensions creating “gridlock in the international governance system, which eventually hinders investments and increases the risk of supply shocks,” he added.
“Ten years on from the global financial crisis, the global economy remains locked in a cycle of low or flat productivity growth despite the injection of more than $10 trillion by central banks. While these unprecedented measures were successful in averting a deeper recession, they are not enough on their own to catalyse the allocation of resources towards productivity-enhancing investments in the private and public sectors,” said the organisation in a statement.
Though some countries advanced significantly in technology integration, the need for skilled workforce and talent adaptability remains crucial as it “pays to enable the workforce to contribute to the technology revolution and to be able to cope with its disruptions.”
The countries should strive towards a “new inclusive and sustainable pathway to economic growth.” It is also important for them to balance economic growth and environmental sustainability, which experts note is possible, citing Sweden, Denmark and Finland as examples.
“Accelerating climate change is already affecting hundreds of millions around the world and it is likely that people under 60 will witness its radical destabilising effects on Earth. In parallel, rising inequality, precocity and lack of social mobility are undermining social cohesion with a growing sense of unfairness, perceived loss of identity and dignity, weakening social fabric, eroding trust in institutions, disenchantment with political processes and an erosion of the social contract,” said the report.
Countries with greater innovation capacity, stronger human capital and better developed infrastructure are more likely to better integrate green energy solutions, though the success is still contingent on policy choices.
More sustainable growth can be generated from countries’ openness and international collaboration, carbon taxes and subsidies, incentives from green research and development and green public procurement.
“Economic growth does not happen in a vacuum. Some basic building blocks are required to jumpstart the development process and more are needed to sustain it. In the current volatile geopolitical context, and with a likely downturn ahead, building economic resilience through improved competitiveness is crucial, especially for low-income countries,” said the report.